How to operate a drone? It’s a question sparking curiosity in many. This guide unveils the intricacies of piloting unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), from understanding basic components and pre-flight checks to mastering advanced maneuvers and capturing stunning aerial footage. We’ll explore essential safety protocols, legal considerations, and troubleshooting techniques, empowering you to confidently take to the skies.
Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your skills, this comprehensive guide provides a structured learning path, covering everything from selecting the right drone and understanding its functionalities to navigating complex airspace regulations. We will break down the process into manageable steps, making the learning experience both enjoyable and informative.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all these essential steps, consult this helpful resource on how to operate a drone to ensure safe and effective flights. Ultimately, responsible operation is paramount for both personal safety and the safety of others.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the basic components of a drone and their functions is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section Artikels the key parts of a typical drone and introduces common terminology used in the drone community.
Major Drone Components and Their Functions
A drone consists of several interconnected components working in harmony. These include:
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate thrust, enabling the drone to take off, fly, and maneuver. Different propeller designs affect flight characteristics such as speed and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors drive the propellers, converting electrical energy into mechanical rotation. Brushless motors are commonly used for their efficiency and longevity.
- Flight Controller: The brain of the drone, this onboard computer receives data from various sensors (gyroscopes, accelerometers, barometers, GPS) and controls the motors to maintain stability and execute flight commands. It’s responsible for everything from basic stabilization to more advanced features like autonomous flight.
- Battery: Provides power to all drone components. The battery’s capacity directly impacts flight time.
- Remote Controller: The pilot uses this device to control the drone’s movements and camera functions. It communicates wirelessly with the drone.
- GPS Module (optional): Allows for precise positioning and autonomous flight modes such as “Return to Home” (RTH).
- Camera (optional): Captures photos and videos. Features vary widely across drone models.
Drone Terminology Glossary
Familiarizing yourself with common drone terms will enhance your understanding and communication with other drone enthusiasts.
- ESC (Electronic Speed Controller): Regulates the speed of each motor individually.
- IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit): Measures the drone’s orientation and movement using accelerometers and gyroscopes.
- RTH (Return to Home): An automated function that guides the drone back to its takeoff point.
- FPV (First-Person View): A flight mode where the pilot sees what the drone’s camera sees through a headset or monitor.
- mAh (milliampere-hour): A unit of battery capacity.
- LiPo (Lithium Polymer): A common type of battery used in drones.
Drone Battery Comparison

Different drone batteries offer varying performance characteristics. Choosing the right battery is crucial for optimal flight time and safety.
| Battery Type | Capacity (mAh) | Voltage (V) | Weight (g) | Approximate Flight Time (minutes) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiPo 3S 1500mAh | 1500 | 11.1 | 150 | 15-20 |
| LiPo 4S 2200mAh | 2200 | 14.8 | 220 | 25-30 |
| LiPo 6S 3000mAh | 3000 | 22.2 | 350 | 30-40 |
| LiHV 4S 2200mAh | 2200 | 16.8 | 200 | 25-35 |
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures: How To Operate A Drone
A thorough pre-flight checklist and adherence to safety procedures are paramount for safe and responsible drone operation. This section details essential steps to ensure a successful and risk-free flight.
Pre-Flight Checklist, How to operate a drone
Before each flight, meticulously check the following:
- Inspect the drone for any physical damage to propellers, motors, or body.
- Ensure the battery is fully charged and properly connected.
- Verify that the remote controller is powered on and correctly paired with the drone.
- Check the GPS signal strength (if applicable).
- Confirm that you have sufficient flight time considering battery capacity and weather conditions.
- Review local drone regulations and airspace restrictions for your flight location.
- Assess the weather conditions. Avoid flying in strong winds, rain, or snow.
- Select a safe and open area for takeoff and landing, away from obstacles and people.
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to handle emergencies is crucial for safe drone operation. Here are some common scenarios and recommended responses:
- Loss of Signal: Most drones have a “Return to Home” (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If RTH fails, visually track the drone and attempt to regain signal.
- Low Battery: Initiate RTH immediately. Land the drone as soon as possible in a safe location.
- Unexpected Malfunctions: Attempt to land the drone safely. If this is not possible, consider using the emergency stop function (if available).
Drone Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to local and national regulations. These rules vary by location and often include restrictions on flight altitude, proximity to airports, and areas with sensitive infrastructure. Always check the specific regulations for your area before flying.
Taking Off and Landing a Drone
Safe takeoff and landing procedures are fundamental to responsible drone operation. This section provides step-by-step instructions and best practices for various environments.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires understanding regulations and best practices. For a comprehensive guide on all these facets, including safety procedures and legal considerations, please refer to this helpful resource on how to operate a drone before your first flight. This will ensure you operate your drone safely and responsibly.
Takeoff and Landing Procedures
The process of taking off and landing a drone can vary slightly depending on the drone model and its features, but the core principles remain the same.
- Pre-flight checks: Complete all pre-flight checks mentioned earlier.
- Find a safe location: Choose a flat, open area away from obstacles and people.
- Arm the drone: Follow the specific instructions for your drone model to arm the motors.
- Takeoff: Gently lift the drone vertically using the throttle stick. Maintain a slow and steady ascent.
- Hover: Practice hovering the drone steadily at a low altitude before attempting more complex maneuvers.
- Landing: Gradually lower the drone vertically using the throttle stick. Aim for a slow and controlled descent.
- Disarm the drone: Once the drone has landed safely, disarm the motors.
Maintaining Stable Control

Maintaining stable control during takeoff and landing requires smooth and precise movements of the control sticks. Avoid sudden or jerky movements that could destabilize the drone.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Some common mistakes include rushing the takeoff and landing process, failing to check the surroundings, and not accounting for wind conditions. Taking your time and carefully assessing the environment before and during flight will significantly reduce the risk of accidents.
Drone Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding drone flight controls is essential for safe and effective operation. This section explains the functions of each control and provides a guide to performing basic maneuvers.
Drone Flight Control Sticks
Most drones use a remote controller with two joysticks. Each stick controls a different aspect of the drone’s movement:
- Left Stick (Throttle/Altitude): Controls the drone’s altitude. Pushing the stick up increases altitude; pushing it down decreases altitude.
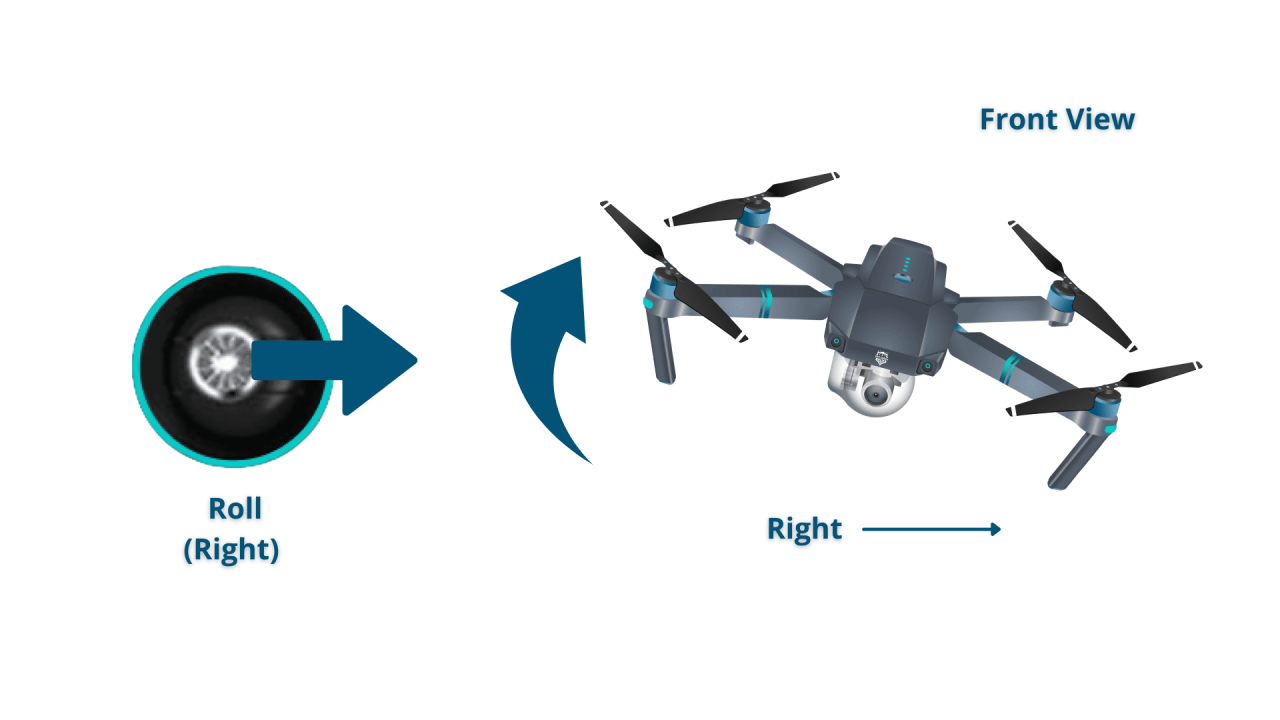
- Right Stick (Yaw/Roll/Pitch): Controls the drone’s orientation. The right stick’s movements control pitch (forward/backward tilt), roll (side-to-side tilt), and yaw (rotation around its vertical axis).
Basic Drone Maneuvers
Once comfortable with the control sticks, you can practice basic maneuvers:
- Hovering: Maintain a steady position in the air without drifting.
- Forward/Backward Flight: Move the drone forward or backward by tilting the drone using the right stick.
- Turning: Rotate the drone by moving the right stick left or right.
- Side-to-Side Movement: Move the drone left or right by tilting the drone using the right stick.
Flight Exercises
Practicing various maneuvers will improve your piloting skills. Start with simple exercises in a safe, open area, gradually increasing the complexity of the maneuvers as your confidence and skills improve.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
Many drones are equipped with cameras capable of capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos. Understanding camera settings and best practices for image capture is crucial for achieving professional results.
Drone Camera Features and Settings
Typical drone camera features include:
- Resolution: The image’s clarity, measured in megapixels for photos and frames per second (fps) for video.
- Video Settings: Frame rate (fps), resolution, and bitrate affect video quality and file size.
- Photo Modes: Different shooting modes like single shot, burst mode, and timelapse offer various creative options.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
To capture stunning aerial photos and videos, consider these tips:
- Composition: Use the rule of thirds and leading lines to create visually appealing images.
- Lighting: Avoid harsh midday sun; shoot during the golden hours (sunrise and sunset) for softer, more flattering light.
- Steady Shots: Avoid jerky movements by using smooth and controlled joystick inputs.
Common Camera Settings and Their Effects
Understanding how different camera settings impact your images is key to achieving desired results. Experiment with different settings to find what works best for you and your subject matter.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are essential for keeping your drone in optimal condition. This section Artikels a maintenance schedule and provides solutions for common problems.
Regular Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule helps prolong the lifespan of your drone and prevent unexpected issues.
- Clean the drone: Wipe down the drone body and propellers after each flight to remove dirt and debris.
- Inspect propellers: Check for any cracks or damage.
- Inspect motors: Check for any signs of wear or damage.
- Check battery health: Use a battery analyzer to monitor battery health and ensure proper charging practices.
- Store properly: Store the drone in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Problems
This table lists some common drone problems, their causes, and potential solutions:
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Drone won’t power on | Low or faulty battery | Charge the battery or replace it with a new one. |
| Motor failure | Damaged motor or ESC | Inspect the motor and ESC for damage. Replace if necessary. |
| Poor signal | Interference or low battery | Move to an area with less interference. Check the battery level. |
| GPS issues | Weak signal or satellite blockage | Fly in an open area with a clear view of the sky. |
Advanced Drone Features and Applications
Modern drones offer a range of advanced features and find applications across diverse industries. This section explores some of these features and applications.
Advanced Drone Features
Advanced features enhance drone capabilities and expand their applications:
- GPS Navigation: Enables precise positioning and autonomous flight modes.
- Obstacle Avoidance: Uses sensors to detect and avoid obstacles during flight.
- Follow-Me Mode: Allows the drone to automatically follow a designated subject.
Drone Applications in Various Industries
Drones are used across many industries, including:
- Photography and Videography: Capturing stunning aerial shots for various purposes.
- Agriculture: Monitoring crops, spraying pesticides, and assessing crop health.
- Construction: Site surveys, progress monitoring, and inspection of structures.
- Search and Rescue: Locating missing persons or assessing disaster areas.
Comparison of Drone Models
Different drone models cater to various needs and applications. Consider factors like camera quality, flight time, features, and price when choosing a drone.
Drone Laws and Regulations
Understanding and complying with drone laws and regulations is crucial for responsible drone operation. This section highlights key aspects of drone regulations.
Key Aspects of Drone Regulations
Drone regulations vary by country and region, but common aspects include:
- Registration: Many jurisdictions require drone registration.
- Flight Restrictions: Restrictions on flight altitude, proximity to airports, and other sensitive areas.
- Privacy Concerns: Regulations regarding data collection and privacy.
- Licensing: Some commercial operations may require specific licenses or permits.
Obtaining Necessary Permits and Licenses
Depending on your intended use, you may need to obtain permits or licenses before operating a drone. Check your local aviation authority for specific requirements.
Consequences of Violating Drone Regulations
Violating drone regulations can result in fines, legal action, and even the confiscation of your drone. Always prioritize responsible and legal operation.
Mastering the art of drone operation opens a world of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to innovative applications across various industries. By understanding the fundamentals of drone mechanics, adhering to safety regulations, and practicing consistently, you’ll develop the confidence and skills to safely and effectively pilot your drone. Remember, responsible operation is paramount – enjoy the flight, but always prioritize safety and legal compliance.
Essential FAQs
What type of drone is best for beginners?
For beginners, a user-friendly drone with GPS stabilization, obstacle avoidance features, and a relatively long flight time is recommended. Look for models with intuitive controls and a good safety record.
How often should I charge my drone battery?
It’s best to charge your drone battery after each flight to maximize its lifespan. Avoid fully depleting the battery as this can reduce its performance and longevity.
What should I do if I lose signal with my drone?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If the RTH fails, try to manually guide the drone back within visual range. If it’s out of visual range, contact local authorities.
Can I fly my drone anywhere?
No. Always check local and national regulations before flying. Many areas restrict drone flight near airports, sensitive infrastructure, and populated areas. Unauthorized drone operation can lead to hefty fines or legal repercussions.
